AI security paper reveals current LLM defense techniques are easily bypassed by adaptive attacks, raising new risks.
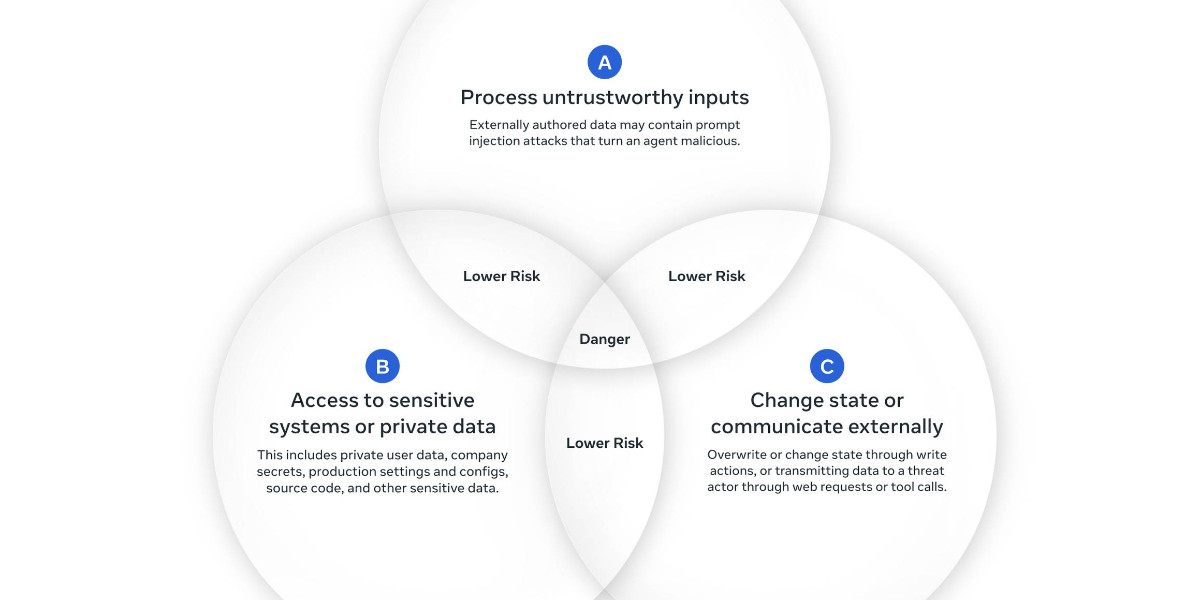
A significant new paper, ‘The Attacker Moves Second: Stronger Adaptive Attacks Bypass Defenses Against LLM Jailbreaks and Prompt Injections,’ demonstrates that existing defenses against prompt injection attacks are much less effective than previously assumed. The research team, representing OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google DeepMind, systematically tested 12 published defense techniques—including those based on randomization, gradient descent, reinforcement learning, and human-guided exploration—and found that most could be bypassed with attack success rates above 90%, even though they initially claimed near-zero vulnerability. Notably, a human red-teaming exercise achieved a 100% success rate, defeating every tested defense[3].\n\nThe findings raise urgent questions about the robustness of LLM security and the potential for malicious actors to exploit these models at scale. The work not only exposes vulnerabilities but also challenges the AI research community to develop more sophisticated, resilient defense mechanisms. With prompt injection attacks posing serious risks for applications relying on LLMs, this research is likely to prompt renewed focus on security hardening and real-world adversarial testing in the AI field[3].
Source: https://simonwillison.net/2025/Nov/2/new-prompt-injection-papers/ Simon Willison (swiss army knife, data, web)
